When collaborating with other applications and libraries, it’s essential to instruct your Integrated Development Environment (IDE), such as Visual Studio, where to locate the required files. This action enables the IDE to recognize available objects, providing programming support, and allows it to reference the files during code compilation.
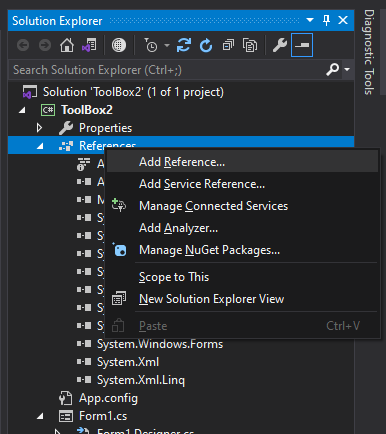
To include a reference in your project, navigate to the Solution Explorer, access ‘References,’ and select ‘Add Reference.’ If the required reference doesn’t appear in the window, you can click ‘Browse’ to manually locate it within the Windows file system.
Autodesk Inventor
Connecting Visual Studio with Autodesk Inventor you need to add reference to the DLL located at:
C:\Program Files\Autodesk\Inventor <Current Version>\Bin\Public Assemblies\Autodesk.Inventor.Interop.dll
If you whish to directly access the objects in the library you can add the following code to the start of the document:
Using Inventor;Imports InventorBoth System.Windows.Forms and Inventor have objects called Application, make sure the code references the correct version.
The following code will then get reference to one instance of the application, and stores it in the variable _invApp. This will first try and connect to any running instances of Inventor, if one cannot be found it will then try to create a new instance.
Application _invApp;
try
{
_invApp = (Application)System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.GetActiveObject("Inventor.Application");
}
catch
{
try
{
Type invAppType = Type.GetTypeFromProgID("Inventor.Application");
_invApp = (Application)Activator.CreateInstance(invAppType);
_invApp.Visible = true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show(ex.Message,"Unable to get or start Inventor");
}
}Dim _invApp as Inventor.Application
Try
_invApp = Marshal.GetActiveObject("Inventor.Application")
Catch
Try
Dim invAppType As Type = GetTypeFromProgID("Inventor.Application")
_invApp = CreateInstance(invAppType)
_invApp.Visible = True
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox(ex.ToString(),, "Unable to get or start Inventor")
End Try
End TryAutodesk AutoCAD
Connecting Visual Studio with Autodesk AutoCAD you need to add reference to the DLLs located at:
C:\Program Files\Autodesk\AutoCAD <Current Version>\Autodesk.AutoCAD.Interop.dll
C:\Program Files\Autodesk\AutoCAD <Current Version>\Autodesk.AutoCAD.Interop.Common.dll
If you whish to directly access the objects in the library you can add the following code to the start of the document:
using Autodesk.AutoCAD.Interop;
using Autodesk.AutoCAD.Interop.Common;Imports Autodesk.AutoCAD.Interop
Imports Autodesk.AutoCAD.Interop.CommonThe following code will then get reference to one instance of the application, and stores it in the variable _Auto. This will first try and connect to any running instances of AutoCAD, if one cannot be found it will then try to create a new instance.
AcadApplication _Auto;
try
{
_Auto = (AcadApplication)System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.GetActiveObject("AutoCAD.Application.24");
}
catch
{
try
{
Type AppType = Type.GetTypeFromProgID("AutoCAD.Application.24");
_Auto = (AcadApplication)Activator.CreateInstance(AppType);
_Auto.Visible = true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show(ex.Message,"Unable to get or start AutoCAD");
}
}Dim _Auto as AcadApplication
Try
_Auto = Marshal.GetActiveObject("AutoCAD.Application.24")
Catch
Try
Dim AppType As Type = GetTypeFromProgID("AutoCAD.Application.24")
_Auto = CreateInstance(AppType)
_Auto.Visible = True
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox(ex.ToString(),, "Unable to get or start AutoCAD")
End Try
End TryAutoCAD.Application.24 only references one version of AutoCAD, you may need to change this to suit your version
Microsoft Office
Office DLLs can be found in the COM tab of the reference manager. you will need ‘Microsoft Office 16.0 Object Library‘ along with the library for the application you whish to use such as ‘Microsoft Excel 16.0 Object Library‘ for Excel.
If you whish to directly access the objects in the library you can add the following code to the start of the document:
using Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel;Imports Microsoft.Office.InteropThe following code will then get reference to one instance of the application, and stores it in the variable _Excel. This will first try and connect to any running instances of Excel, if one cannot be found it will then try to create a new instance. This code can easily be adjusted to other office programs by simply replacing Excel with your desired application.
Excel.Application _Excel;
try
{
_Excel= (Excel.Application)System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.GetActiveObject("Excel.Application");
}
catch
{
try
{
Type AppType = Type.GetTypeFromProgID("Excel.Application");
_Excel = (Excel.Application)Activator.CreateInstance(AppType);
_Excel.Visible = true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show(ex.Message,"Unable to get or start Excel");
}
}Dim _Excel as Excel.Application
Try
_Excel = Marshal.GetActiveObject("Excel.Application")
Catch
Try
Dim AppType As Type = GetTypeFromProgID("Excel.Application")
_Excel = CreateInstance(AppType)
_Excel.Visible = True
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox(ex.ToString(),, "Unable to get or start Excel")
End Try
End Try
Leave a Reply